Antidepressants are a cornerstone of treatment for depression and anxiety, but does your brain go back to normal after antidepressants? Antidepressants work by increasing certain chemicals in your brain called neurotransmitters, which are responsible for your mood. Unfortunately, this is not an immediate process.
It takes two to three weeks for the effects to be felt, and unfortunately, many people give up on antidepressants before that. However, there is also research that suggests that taking antidepressants may have long-term consequences on the brain – making you more prone to depression and anxiety after you stop taking them. Does the brain go back to normal after antidepressants?
Eventually, the brain readjusts and thus goes back to normal after antidepressants via neuroplasticity, but withdrawal symptoms may occur since the process causes a rapid change in the brain chemicals and functioning that had been adjusted. However, there are no guarantees that the brain will go back to normal after antidepressants because different people have different ways of brain function.
There’s no easy answer to whether your brain will go back to normal once you stop taking an antidepressant, but we’ve got some information for you.
Contents
Does your brain go back to normal after antidepressants?
But some experts say that although the withdrawal effects can be prolonged, the brain goes back to normal with time – though there are no guarantees. Your brain takes time to readjust but most people do experience a return to their normal brain state. However, no one knows what will happen when you stop taking an antidepressant because it varies between individuals and depends on factors like how long you’ve been taking them or what type of drug you were using.
Neuroplasticity, which is the ability of the brain to modify, change, and adapt both structure and function throughout life and in response to experience, aids the brain to go back to normal after stopping the medication. It is the same process that helps the brain to adapt to the new levels of brain chemicals when you are using antidepressants.
It is important to note the time factor that it takes for the brain to go back to normal varies from individual to individual. It may also be dependent on the length of time on antidepressants, type, and dose of the antidepressant being taken among others.
There are many people who have very positive experiences with antidepressants. For example, some people take antidepressants for just a few months at the beginning of their treatment for depression and anxiety disorders. Then, after seeing that their depression is manageable, they stop taking the medication. But if you’ve been taking an antidepressant for years, it might be difficult to stop taking it cold turkey.
One study found that 20 weeks was the median time needed for half of the participants to withdraw from their antidepressant drug.
How Long Does it Take for Your Brain to Go Back to Normal after stopping antidepressants?
The time it takes for someone who has taken antidepressants to feel back to normal can vary based on their individual brain chemistry. There is no hard and fast rule about the length of time that it takes for your brain to return to normal after stopping antidepressants.
The best thing for people to do is research the medication that has been prescribed in order to learn more about how it affects the body, and then make a decision.
For some people, it may take six months before they feel back to normal after going off antidepressants. However, other people may not see a difference at all and continue struggling with their mental health even though they have stopped taking their medication.
As with any type of medication, antidepressants can come with side effects that may include:
- feelings of anxiety or restlessness;
- insomnia (difficulty sleeping);
- fatigue;
- thoughts of suicide;
- weight gain or loss;
- sexual dysfunction; and
- general malaise.
While many people who stop taking antidepressants may experience side effects, there are ways to minimize these symptoms by gradually tapering off the dosage until you’re no longer on them at all.
What influences how long it takes for the brain to adjust after stopping antidepressants
While antidepressants can be life-changing for people who have a mental health disorder, the long-term use of these drugs can have negative side effects.
There’s no easy answer to whether your brain will go back to normal once you stop taking an antidepressant, but we’ve got some information for you.
We know that withdrawal symptoms are fairly mild in the first one to three days and may intensify on the fourth or fifth day before they subside and may persist for up to three weeks.
However, there is still concern about anxiety or depression relapse making the symptoms worse.
What is antidepressant withdrawal?
Antidepressant withdrawal is a condition characterized by the return of depressive symptoms and anxiety disorders after a period of time following the use of an antidepressant. The most common side effects of antidepressants are decreased sex drive, weight gain, and headaches.
Most experts agree that if you stop taking an antidepressant without discussing it with your doctor first, it’s likely that you’ll experience some form of withdrawal or side effects.
Antidepressants can also cause problems with erectile dysfunction, but they do not always do so. Anxiety and depression are both conditions that require treatment to manage symptoms. Antidepressants offer relief from these conditions for millions of people, but there is no easy answer to whether or not your brain will go back to normal once you stop taking them.
There are many factors as to why someone may want to discontinue their use of antidepressants including:
- adverse effects on health;
- financial considerations;
- fear of addiction;
- fear for physical safety on account of being in an abusive relationship;
- difficulty engaging in activities one enjoys;
- difficulty concentrating at work or school;
- difficulty sleeping and/or lack of energy.
The good news is there are several things you can do to minimize the chance that the discontinuation process will be too difficult – like slowly tapering off the medication over time. It’s important to talk through your options with your physician before making any decisions about your medical care (e.g., stopping treatment).
Time for antidepressants to leave your system
Discontinuation symptoms usually go away within a few weeks of discontinuing the medication but the length that it takes the antidepressant to leave the system depends on the half-life of the medication.
This is as per the chart below:
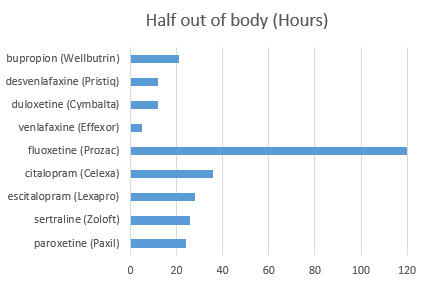
To get 99% of the drug from your system, it takes a number of days for most antidepressants. The time it takes for the drug to clear from your system is as per the chart below:
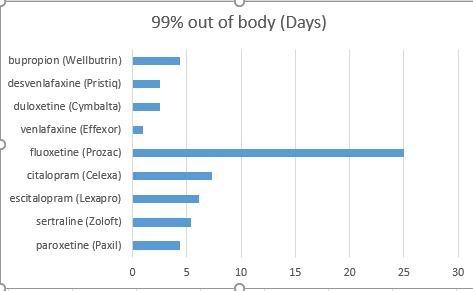
You may experience discontinuation symptoms, like brain zaps, memory loss, and headaches, but these should go away within a few weeks of discontinuing the antidepressant. It’s important to speak with your doctor about how your body can best recover from taking an antidepressant for a long time.
The time that antidepressant withdrawal lasts
If you stop taking an antidepressant, you might experience withdrawal symptoms. These symptoms usually last between 3-6 weeks. They will subside on their own without any medical treatment.
But, like other withdrawal symptoms, they can be uncomfortable while they’re happening. Antidepressants are a lifelong treatment for some people with depression and anxiety disorders, but if you’ve been taking them for a long time (more than 2 years), talk to your doctor about weaning off the medication gradually to minimize discontinuation symptoms.
There are a lot of reasons why antidepressants may be prescribed for someone who doesn’t need them anymore. It could be because you no longer have the disorder that made it necessary in the first place, or because your dose is too high and needs to be lowered.
Your doctor knows best how long to prescribe an antidepressant based on your needs as an individual and what’s right for your brain and body as well as your mental health condition.
Why does antidepressant withdrawal take so long?
Because the body may react to the reduction of available serotonin in the brain causing the discontinuation syndrome which has emotional and physical symptoms. The symptoms range from a feeling of the mind being “foggy” to flu-like symptoms, such as queasiness, dizziness, and headaches.
These symptoms usually start within one or two days after you stop taking your antidepressant and can last for weeks. In most cases, the symptoms gradually subside over time, but it can take months before they do.
While antidepressants are life-changing for people who struggle with mental health disorders, they also come with side effects that could last long after you stop taking them.
There’s no easy answer to whether your brain will go back to normal once you stop taking an antidepressant, but we’ve got some information for you.
Do you feel better after stopping antidepressants?
You might feel better, or you might not. Some people with depression will feel worse after they stop taking antidepressants because their brain goes into withdrawal. Others may notice that they don’t have the same highs and lows as before and even experience a more stable mood.
Regardless of which side effects you experience, there are always other treatment and coping options that can help you combat your anxiety disorder or depression if you decide to stop taking an antidepressant.
It’s important to remember that your mental health is a lifelong journey and it’s not about just one medication. There are many types of treatments available today, from therapy to mindfulness apps, that can help alleviate your mental health struggles. The key is finding what works best for you.
What happens to your brain after you stop taking antidepressants?
After you stop taking antidepressants, your body may develop physical and/ or emotional symptoms of low serotonin levels in the brain. These symptoms can include headaches, nausea, dizziness, or a feeling of unease.
The brain’s serotonin levels regulate our mood and sleep cycles. As soon as you stop taking an antidepressant, your serotonin levels might go back down and affect your mood. And not all antidepressants are the same; some people find that their brain goes back to normal after antidepressants while others don’t.
Sometimes doctors will give patients a low dose of an SSRI (selective serotonin reuptake inhibitor) for a period of time to help the patient’s brain adjust to life without antidepressants.
Potential side effects of stopping antidepressants
One of the most common side effects of stopping antidepressants is a “brain zap,” which is a sudden burst of anxiety and panic.
Another possible side effect may be withdrawal symptoms from the medication. This can cause symptoms like dizziness, nausea, and muscle aches. In some cases, people experience depression again after they stop taking their antidepressants.
It’s important to talk with your doctor before you quit taking an antidepressant to make sure you have an effective plan in place. Your doctor will create a treatment plan with you that will gradually wean you off the medication while also addressing any other issues that might occur due to withdrawal or discontinuation of therapy.
Can stopping antidepressants cause you to relapse?
It’s normal to feel anxious, fatigued, and irritable when you stop taking an antidepressant. The good news is that the symptoms typically go away after a few weeks.
According to a study published in BMJ Journal, more than half of the people who stop taking antidepressants (56%) after a long-term usage experience a relapse within a year as compared to 39% of the people who are still using the medication. Therefore, stopping the medication can lead to a relapse if not well managed and replaced with other methods of treating anxiety disorders and depression.
However, people who have used antidepressants for a long time have a reduced risk of relapse as compared to short-time users. One of the main reasons for the relapse is the withdrawal symptoms. And thus, the drug should be tapered off to reduce instances and severity of withdrawal symptoms.
Even though the cases of relapse are quite high, discontinuation does not lead to a uniform occurrence of relapse. Therefore, doctors should treat each case as a special case to determine the individual relapse risk.
There are also many things you can do to help your body adjust to the changes of stopping antidepressants. If you do start feeling worse after you stop taking them, then it may be time to talk with your healthcare provider.
What should you do if you want to stop taking your antidepressant?
There are a few strategies you can use to help ease the discomfort of withdrawal.
- Start with reducing your dosage with a low dose and gradually reduce your dosage over time.
- Talk to your doctor about weaning off antidepressants.
- Exercise, get enough sleep, and practice meditation or yoga.
- Get support from family and friends.
- Take care of yourself.
- Join a support group
- You can take another treatment method such as counseling or psychotherapy techniques such as CBT
Length to come off antidepressants
It is important that you talk to your doctor about how long it will take for the antidepressant to leave your system but generally, it takes 4 weeks, but sometimes longer. There are many antidepressants, and they all work a little differently.
Depressive disorders can manifest themselves in different ways, so some people might find it easier to withdraw from an antidepressant than others. Some antidepressants make you feel more energized and able to focus, while others have a more sedating effect on the body.
When coming off antidepressant medication, it’s important to remember that mood swings are normal and will pass over time. If you’re experiencing any unusual side effects while withdrawing from antidepressants, please talk to your doctor immediately.
The best thing you can do is be patient with yourself by taking things one step at a time as you come off of antidepressant medication.
Can antidepressants permanently change your brain?
Yes, antidepressants can permanently change your brain. The first thing to understand is that antidepressants change your brain. It takes a long time for those changes to go back to normal, and sometimes they don’t go back to normal at all. The second thing you need to understand is that the brain is constantly changing anyway.
Your brain is always changing and adapting…and no one knows how it will change without medication. We do know, however, that the way it changes without medication won’t be as good–and that’s why people take antidepressant medications in the first place.
Can antidepressants rewire your brain?
Yes, it appears that SSRI antidepressants rewire areas of the brain. The rewiring process is not an instantaneous one. It’s a gradual one that takes place from weeks to months after the person stops taking the drugs.
Some people believe the rewiring process has a negative impact on their brains, which can lead to problems like memory loss or difficulty concentrating. But others argue that antidepressants don’t change your perception and make you feel better.
Research suggests that SSRI antidepressants do in fact change parts of the brain, but these changes are not harmful to your overall health as long as you stop taking the drug and allow time for your brain to go back to normal.
Long-term effects of antidepressants
One of the most common side effects of antidepressants is weight gain. Some people may also experience sexual dysfunction, sleep problems, and changes in appetite.
It’s difficult to go off antidepressants because there are those long-term side effects that make it tough to discontinue the drugs.
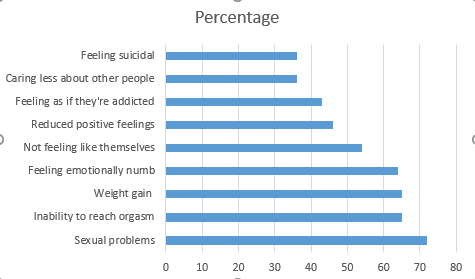
These side effects can make your brain go back to normal once you stop taking an antidepressant, but that’s not always the case. Your brain will only return to normal if it’s been altered by the drug, which happens more often than not.
If you want to avoid these negative side effects, discuss other options with your doctors like counseling therapy or cognitive-behavioral therapy (CBT). These treatments have been proven effective in treating mental pain and anxiety disorders. Your brain will never go back to normal if you stay on antidepressants for too long, so be sure to be mindful when using them.
There are different types of antidepressant drugs, with each targeting a specific type of serotonin or norepinephrine receptor and having its own side effects and risk of relapse. Antidepressants can help ease the pain and struggle of depression, but many people worry that once they stop taking them, they’ll go back to struggling with their mental health. That’s natural.
Even though antidepressants are life-changing for people who struggle with depression and anxiety disorders, the long-term use of these drugs can have negative side effects.
Do antidepressants change your personality?
We’ve all seen commercials that show a person who is sad and withdrawn, and then they take an antidepressant and they’re suddenly happy. There are many misconceptions about how antidepressants work.
For example, “do antidepressants change your personality?” The short answer is no. When taken correctly, antidepressants will not change your personality. One common misconception is that people who take antidepressants are always happy.
Although it may seem like this in some commercials, it’s not true. Antidepressants promote feelings of contentment and calmness for those who suffer from depression or anxiety disorders, but that doesn’t mean you can’t experience feelings of sadness or anger while taking an antidepressant.
And if you do experience these emotions, it doesn’t mean the medication isn’t working or that you need to increase your dosage or try a new type of antidepressant; these emotions should be treated as normal responses to stressful life events.
Conclusion
You might be worried that your brain won’t go back to normal after you stop taking an antidepressant, but it’s not a sure thing. With a lot of research and willpower, your brain will eventually go back to how it was before you were on the medication.
It can take time, though. You might need to work with a psychiatrist or therapist who specializes in cognitive-behavioral therapy (CBT). This therapy has been shown to help people who are recovering from depression and anxiety disorders by teaching them new skills.
Research on CBT has shown that it reduces the recurrence rate for people who have had one episode of depression or anxiety disorder by 50 percent over other types of treatments.
We understand that it’s a stressful experience when deciding whether to take an antidepressant for your mental health. But, if you’ve been struggling with depression, anxiety, or any other mental health concern, you should know that antidepressants are life-changing.
These drugs have helped people who have suffered from these conditions and have made their lives better. Once you start taking an antidepressant, it will most likely change your brain chemistry and make it so that you need the drug to function properly.
The good news is that there are some steps you can take to help get rid of these antidepressants before they become long-term use. There are many different methods like diet changes and reducing stress that could help you get off the drugs quicker than expected.
FAQs
What is the damage caused by antidepressants?
Antidepressants are a huge part of the mental health world. They can help regulate your brain chemistry and ease depression symptoms. But they also have some negative side effects, like weight gain, sexual dysfunction, and sleeplessness. They can also actually hinder long-term recovery efforts if you take them for too long. Long-term use of antidepressants can change the way your brain works, making it more difficult for you to get back to normal once you stop taking them. This is because antidepressants cause changes in the way your brain reacts to serotonin. For example, antidepressants may make it harder for your brain to produce serotonin on its own without the medication’s help. When you stop taking an antidepressant after long-term use, the depressive symptoms may come back even stronger than before because of this problem with serotonin production.
Will my brain go back to normal after taking antidepressants?
It’s tough to say. There are studies that show when people stop taking certain antidepressants, their depression symptoms start to show again. That being said, other research shows that people who have taken antidepressants for a long time may have better moods after stopping them.
Can I take an antidepressant if I don’t have depression or anxiety?
No. Antidepressants are only for people with diagnosed depression and anxiety disorders. They can also be used in cases of Bipolar Disorder, ADHD, and OCD, but it needs to be prescribed by a doctor first.
How do I know if my brain will go back to normal once I stop taking an antidepressant?
We don’t know, unfortunately. There is not enough data available on the subject because it hasn’t been studied enough, but there are some trends we can look at based on existing data, and patients who have visited our clinic often recover but with other help such as counseling, psychotherapy, self-awareness, exercise, getting a companion among others.
Citations:
https://www.health.harvard.edu/diseases-and-conditions/going-off-antidepressants