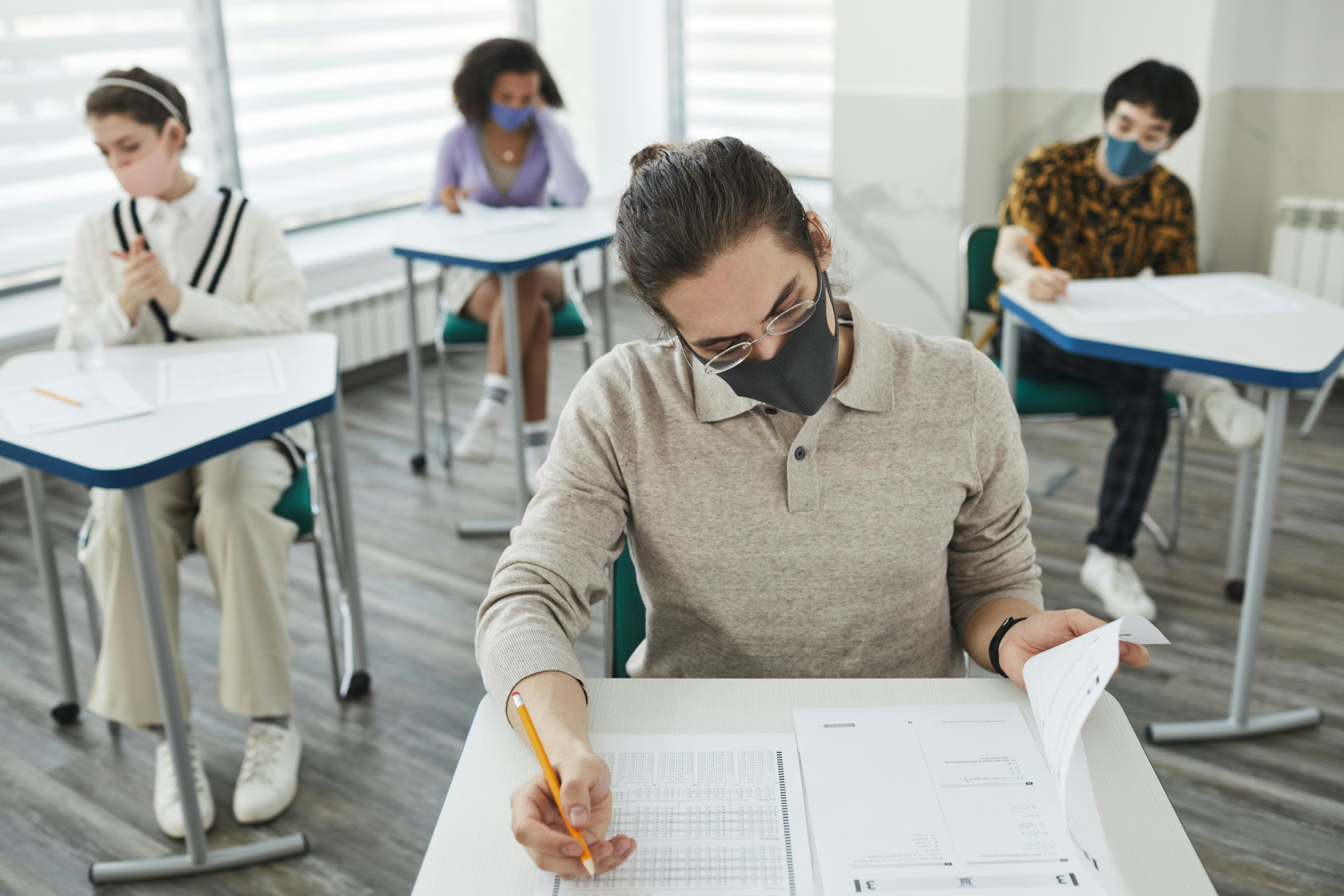
Test anxiety is a feeling of nervousness or fear experienced by students when facing a test or exam. It’s a type of performance anxiety that negatively impacts student performance. Test anxiety is actually a type of performance anxiety where fear and anxious moments emanate from a situation where the performance really matters or when there is a lot of pressure to perform well, especially in examinations and other instances.
Test anxiety can be particularly challenging for students who are sensitive to stress and anxiety in general. The pressure of knowing the answers and needing them to move forward can create an intense sense of fear at the thought of failing or not doing well enough.
Test anxiety is not only common but also completely natural, even among adults. Even though we don’t like admitting it, everyone experiences test anxiety from time to time. However, it doesn’t have to be this way.
Contents
What is Test Anxiety?
It is a type of performance anxiety that emanates from situations where you need to perform like in examinations or where expectations are high that you will perform well.
Test anxiety can be particularly challenging for students who are sensitive to stress and anxiety in general. The pressure of knowing the answers and needing them to move forward can create an intense sense of fear at the thought of failing or not doing well enough.
Test anxiety is not only common but also completely natural, even among adults. Even though we don’t like admitting it, everyone experiences test anxiety from time to time. However, it doesn’t have to be this way.
What type of anxiety is test anxiety?
Test anxiety is a type of performance anxiety. Performance anxiety is a feeling someone might have in a situation where performance really counts or when the pressure’s on to do well.
The pressure of knowing the answers and needing them to move forward can create an intense sense of fear at the thought of failing or not doing well enough. This fear can be particularly challenging for students who are sensitive to stress and anxiety in general.
Types of test anxiety
Test anxiety can manifest in two ways: cognitively or somatically. Cognitive test anxiety is what we already talked about. It’s the fear of not doing well, not knowing the answers, etc.
Somatic test anxiety is a physical response to cognitive anxiety. This can include everything from shaking hands and sweaty palms to shakiness in your voice.
Cause of Test Anxiety

The cause of test anxiety is often a combination of the following factors:
- Poor study habits: Students may not have studied thoroughly enough and are worried that they won’t know the material.
- Poor past test performance: The student has found past tests or exams difficult and is worried about repeating the same experience.
- Underlying anxiety problem: This type of anxiety may be caused by an underlying psychological condition such as generalized anxiety disorder (GAD) or panic disorder – in these cases, it’s important to seek professional help.
- Fear of failure:
Signs that your student may have Test Anxiety
Here are some signs that your student may be experiencing test anxiety:
1. Emotional Symptoms:
- Feelings of stress, fear, helplessness, and disappointment: Your student may exhibit signs of increased stress and fear leading up to tests. They might express a sense of helplessness or disappointment about their performance.
- Negative thoughts: Your student may engage in rumination, constantly thinking about past poor performances and the potential consequences of failure. They may feel inadequate or helpless in relation to their exams.
2. Physical Symptoms:
- Headache, nausea, excessive sweating: Your student might experience physical discomfort such as headaches or feelings of nausea before or during tests. Excessive sweating can also be a physical manifestation of test anxiety.
- Shortness of breath, rapid heartbeat: Test anxiety can cause physiological changes, including shortness of breath and an accelerated heartbeat. These symptoms may become more pronounced during exams.
- Lightheadedness, feeling faint: Your student may feel lightheaded or on the verge of fainting due to heightened anxiety during tests. It is important to address these physical symptoms promptly.
- Panic attacks: In severe cases, test anxiety can trigger panic attacks characterized by sudden intense fear or discomfort. These panic attacks may involve difficulty breathing and a sensation similar to having a heart attack.
3. Behavioral/Cognitive Symptoms:
- Difficulty concentrating: Your student may struggle to maintain focus and concentration during tests. Test anxiety can impair cognitive function and make it challenging to process information effectively.
- Thinking negatively: Test anxiety can lead to negative thought patterns, such as self-doubt and self-criticism. Your student might engage in negative self-talk or have a pessimistic outlook about their abilities.
- Comparing oneself to others: Test anxiety may drive your student to constantly compare themselves to their peers. This comparison can further contribute to feelings of inadequacy and increased stress.
- Procrastination: Students with test anxiety may resort to procrastination as a coping mechanism. They might delay studying or avoid preparing for exams due to the overwhelming anxiety associated with them.
It’s important to note that experiencing one or more of these symptoms does not necessarily mean that a student has test anxiety. However, if you notice a consistent pattern of these signs and it significantly affects your student’s academic performance and well-being, it may be beneficial to seek support from a school counselor, teacher, or mental health professional to address their test anxiety effectively.
Effects of test anxiety
The effects of test anxiety are different for each student but the common symptoms of test anxiety are headache, nausea, excessive sweating, shortness of breath, rapid heartbeat, lightheadedness, and feeling faint. Some students may experience one or two while others may experience more.
One way to get rid of these effects is by understanding the cause and knowing that it’s not a sign of weakness. Sometimes, the stress and anxiety can be due to thoughts about how you will do on the test, how your parents might react if you don’t do well, or what people will think of you if you mess up.
Students who experience test anxiety should know that it’s not a sign of weakness and there are ways to lessen its effect on them. There are many strategies that can help students cope with their anxiety, but first, they must understand the source of their fear so that they can tackle it and get over it.
How common is test anxiety?
Test anxiety is a common feeling that many students experience before, during, or after taking a test. It can be distracting, unsettling, and detrimental to student performance. The American Psychiatric Association estimates that between 40 and 60% of students have significant test anxiety that interferes with their performance in examinations and tests.
Test anxiety is majorly common in students who have not prepared well, have a previous failure in exams, are doing the examination in unfamiliar territory, or have other anxiety disorders.
What can you do to help your students with test anxiety?
There are several ways that a student can conquer test anxiety. They include:
- It can help students to learn how to study efficiently. Studies have shown that there is a correlation between test anxiety and poor grades, so it’s important that you focus on studying more before the big test.
- Studying early and in similar places can be helpful as well.
- It helps students get into the same routine each time they study, which in turn makes them feel more confident and less anxious before tests. Establishing a consistent pretest routine is also very important, as routines create a sense of stability and peace of mind.
- Talking to your teacher about your feelings of unease over taking tests can help — they might be able to provide some insight or support by helping you work through any issues you are experiencing with test anxiety.
- Learning relaxation techniques might also be an excellent way to reduce your stress levels, like deep breathing exercises or meditation.
- Another tip that might help those with test anxiety is to not forget to eat and drink. Eating healthy foods before sitting down to take a big exam will help students stay focused and alert throughout the entire test.
- Getting some exercise before exams can also make students feel better prepared for the day ahead, plus it releases endorphins which have been shown to reduce stress levels (plus don’t forget about the health benefits!).
- Lastly, getting plenty of sleep will improve your ability to think clearly on an empty stomach, so try going to bed early the night before an exam!
Strategies to reduce test anxiety in the Classroom
There are many strategies you can use to reduce test anxiety in the classroom. They include:
- Hand massage is a great way to relax and ease the tension in your body.
- Another strategy is to let out some deep sighs while taking slow, deep breaths.
- Another strategy is to try flotation therapy, which involves floating on water and would help reduce one’s weight of study like studying for an exam or taking a test.
- You could also practice muscle relaxation by focusing on relaxing each part of your body as you go through it and making sure it’s loose when finished.
- Listening to calming music can be helpful and exercising reduces anxiety as well as settles nerves.
- Prayer or meditation can also help calm nerves and keep perspective.
Helping Students Manage Test Anxiety Outside of Class
When I teach a test, I’ll often tell my students to do something physical before they come in. Exercise, meditation, and deep breathing are great options because they help relieve stress. I also recommend that my students bring a form of calming music to play during the test or exam.
You can talk to your child’s teacher about the possibility of setting up an MP3 player at their desk or in the testing area so they can listen to music while they take their test. This alleviates anxiety by providing an escape from the worries and stresses of the moment.
Who will likely have test anxiety?
Most people experience test anxiety as they begin school but it rises sharply in students in Grades 2 to 4. It thereafter remains high during middle and high school. In fact, it peaks at around 18 years old. If your child is currently experiencing test anxiety, there are a few things you can do to help them.
One of these methods is taking deep breaths and breathing from the stomach. Deep breathing exercises won’t cure their anxiety, but they will help them get through the exam or test with less panic and stress.
Poor grades and missed opportunities are just some of what can happen with chronic test anxiety. If your child is struggling with test anxiety and needs assistance, it’s important to seek professional help from a licensed therapist as soon as possible because this type of performance anxiety can be detrimental for students for the rest of their lives if left untreated.
Why is Test Anxiety so Common?
Test anxiety is a common phenomenon for several reasons:
- Uncertainty and Outcome Predictability: Tests often represent high-stakes situations where the outcome can significantly impact academic performance, grades, and future opportunities. The uncertainty surrounding the test results can trigger anxiety, as students may feel pressured to perform well without being able to predict the exact outcome.
- Academic Pressure: Students may face substantial academic pressure from various sources, including parents, teachers, and themselves. The expectation to excel academically can create a fear of failure and contribute to test anxiety.
- Perceived Lack of Preparation: If students feel unprepared or believe they have not studied enough for a test, it can lead to a sense of helplessness and anxiety. They may worry about their ability to recall information accurately or perform at their desired level, which can intensify their anxiety.
- Fear of Negative Consequences: Students may fear the potential consequences of poor test performance, such as receiving a low grade, disappointing their parents or teachers, or hindering future opportunities. This fear can further contribute to test anxiety.
- Guilt and Self-Imposed Pressure: When students recognize that they have not met their own expectations or responsibilities in terms of studying or preparation, they may experience feelings of guilt. This self-imposed pressure to meet their own standards can intensify test anxiety.
- Social Comparison: Students may compare themselves to their peers, which can fuel anxiety if they perceive themselves as falling behind or not measuring up to others’ performance. The fear of being judged or negatively evaluated by their peers can contribute to test anxiety.
Is there medicine for test anxiety?
Beta-blockers such as propranolol are effective medications for test anxiety since they are fast-acting medications for anxiety. This medication is usually used for people with high blood pressure, but it’s also prescribed for people who have performance anxiety. It slows the heart down and stops some of the physical symptoms of anxiety-like shaking.
Is test anxiety a mental illness?
Yes, it is a performance anxiety type of mental illness. What is test anxiety and how can students with it? Test anxiety is a type of performance anxiety that negatively impacts student performance. The pressure of knowing the answers and needing them to move forward can create an intense sense of fear at the thought of failing or not doing well enough.
Test anxiety is not only common but also completely natural, even among adults. Even though we don’t like admitting it, everyone experiences test anxiety from time to time. However, it doesn’t have to be this way.
Why do I feel like vomiting after studying?
The nervousness or fear of failing can lead to feelings of nausea, weakness, shaking hands, and sweaty palms. Moreover, Cramming and studying without taking a rest or a long time can cause sickness including vomiting.
Actually living with test anxiety is not only uncomfortable but it can also be detrimental to your grades. If you find yourself in an intense bout of stress before an exam or test, it might be time to take a break before the situation gets worse.
Take deep breaths and do some relaxing activities like meditation or yoga to help calm down. Practice a few calming exercises that are specific to your test anxiety so that you know what works best for you and always have them on hand when you need them. And don’t forget to eat healthily and get plenty of sleep!
Conclusion
Test anxiety is a type of performance anxiety that negatively impacts student performance. But it doesn’t have to be this way! High-quality academic support, like an essay writing service, can help students succeed even in the face of test anxiety.
If you’re a student and don’t know how to overcome test anxiety, here are some tips that might help:
- Create a study plan
- Take timed practice tests
- Eliminate distractions while studying
- Get enough sleep the night before the test
- Eat breakfast before the test
FAQs
Can test anxiety be cured?
No. The best way to combat test anxiety is by preparing for the event. The more knowledgeable a student is about the test and what they need to do, the more prepared they will be to tackle it head-on.
What should I do when I have a test coming up?
Prepare yourself! Make sure you understand the material thoroughly and know how to answer any questions that might come up. You can also try looking at past tests from previous years and use them as study guides or practice tests. Looking at past tests not only helps you prepare for upcoming exams but also gives insight into different types of questions and topics that might come up. Taking deep breaths can help relieve some of the pressure and calm your nerves. Avoiding caffeine before taking a test can also help with performance anxiety by reducing jitters. Someone who experiences mild anxiety may find relief in eating small, frequent meals containing complex carbs like pasta, whole grains, vegetables, or fruit before an exam as this will provide energy and nutrients while stabilizing blood sugar levels.
What are the most common causes of test anxiety?
The most common causes are a lack of study, not being prepared for a test, or worrying about future tests. In addition, students with other anxiety disorders are more prone to test anxiety as compared to others.
How can I help my students with test anxiety?
There are many things teachers and parents can do to help students with test anxiety. One way is to give them more time on tests and exams. Another way is to provide positive feedback after a test or exam. This will show students that they did well and should be proud of themselves. Teachers can also set realistic expectations for their students to take away any unnecessary pressure. Other things teachers/parents can do include providing extra help as needed in small group sessions, encouraging the student to work through their fears one step at a time, and reminding them that they have been successful in the past.
Can you take Xanax before an exam?
Yes, Xanax is good for performance anxiety. You can take Xanax an hour before the exam for maximum benefits. Xanax will be able to take care of the test anxiety cognitive symptoms like worrying about performance or dread emanating from past experiences