Anxiety disorders are common mental disorders that can present with symptoms in several body parts. But what does anxiety back pain feel like? Do you ever feel like your back is against the wall?
Anxiety back pain can either feel like a burning sensation in the back or sharp, shooting, or stabbing pain causing back stiffness. Anxiety can cause muscle tension, inactivity, changes in posture, and other back changes that cause back pain. The anxiety back pain can disrupt sleep, cause immobility, and increase pressure in the back.
It tends to happen when you’re feeling anxious about something. With anxiety, a person can experience persistent aches or stiffness at any spot on the spine length. Chronic anxiety can cause you to experience intense back pain in a variety of circumstances. This article covers the different types of anxiety-related back pain and their potential causes, diagnostic processes, and treatment methods.
Contents
What is Anxiety Back Pain?
Anxiety back pain refers to the experience of back pain either on the lower or upper back that is linked to heightened levels of anxiety and stress. While anxiety itself may not directly cause structural issues in the back, it can lead to muscle tension and other physiological responses that contribute to discomfort and pain in the back area. The relationship between anxiety and back pain is complex and can vary from person to person.
Here’s a breakdown of how anxiety can contribute to back pain:
- Muscle Tension: Anxiety triggers the body’s “fight or flight” response, causing muscles to tense up in preparation for a perceived threat. This muscle tension can extend to the muscles of the back, leading to stiffness, soreness, and even spasms.
- Hypervigilance: Anxiety often leads to hypervigilance, where individuals are excessively focused on potential threats or dangers. This heightened awareness can cause individuals to hold their bodies in tense postures, leading to increased muscle strain and discomfort.
- Alteration of Breathing Patterns: Anxiety can affect breathing patterns, causing individuals to take shallow breaths or even hyperventilate. This can impact the oxygen supply to muscles, potentially leading to muscle tension and pain, including in the back area.
- Contributing Lifestyle Factors: People experiencing anxiety may also engage in behaviors that contribute to back pain, such as poor posture, lack of physical activity, or engaging in activities that strain the back muscles.
- Central Sensitization: Chronic anxiety can lead to a phenomenon known as central sensitization, where the nervous system becomes more sensitive to pain signals. This can result in heightened pain perception, including in the back region.
In many cases, anxiety-related back pain occurs in people who have an existing back problem. Stress can aggravate existing back pain and lead to the development of new problems.
How Does Anxiety Cause Back Pain?
People who have anxiety disorders experience more physical symptoms than those who have other mental health issues. Anxiety disorders are characterized by persistent and excessive worry, often accompanied by restless behavior and difficulty concentrating.
The most common anxiety disorders are generalized anxiety disorder (GAD), social anxiety disorder (SAD), panic disorder, and obsessive-compulsive disorder (OCD). Experiencing chronic stress can lead to many physical symptoms — including back pain.
Back pain can be caused by stress or anxiety in a couple of ways: Chronic stress may lead to muscle tension, which can cause back pain. Stress can also trigger a fight-or-flight response. This response is intended to be short-term but can cause long-term issues if it becomes chronic.
Back pain can be associated with breathing patterns and effects on the muscles change and cause strain and tension in the mid-back or the curling of the body during anxiety moments. Anxiety thus may cause tension in the muscles in the upper or lower back thus causing back pain.
What does anxiety back pain feel like?

Anxiety back pain feels like either a burning sensation on the back or pain in any section of the spine. Anxiety-related back pain is generally characterized by a feeling of tightness or achy soreness in the low back and/or the upper back.
People who have anxiety-related back pain report that the pain can come and go — sometimes going away for days or weeks before returning.
And, sometimes the pain is accompanied by other symptoms, including:
- Muscle spasms
- Muscle cramping
- Muscle tension
- Joint pain
These symptoms are often worse when stress is high and better when it is low. Back pain as a result of anxiety can vary depending on which muscles are affected.
Generally speaking, anxiety back pain will be located in your upper or lower back and will feel like constant, aching pain. Your anxiety back pain may also cause pain that extends into your neck or shoulders.
How long does anxiety back pain last?
The length of the anxiety back pain depends on the frequency of the attacks, whether there were some back pains before the anxiety, how severe the anxiety attack is, whether the underlying stress was addressed, and also how previous episodes of anxiety attacks behaved. Anxiety-related back pain can last just a few minutes to weeks or months, depending on the person and the circumstances
However, a single episode of anxiety back pain can last for 20 minutes or more since it takes that amount of time for the body to recover from a major stress response. The pain may persist or worsen over time if the underlying stress is not addressed.
The level of stress and anxiety is often the deciding factor. Anxiety causes muscle tension and can increase the level of cortisol in the body.
Increased cortisol levels can lead to pain and tension in the muscles and cause stiffness. Long-term or frequent anxiety-related back pain can indicate that someone is experiencing health issues associated with anxiety. It can also indicate that the person needs to make some changes to manage their anxiety better or seek treatment for anxiety.
Why does anxiety cause back pain?
Anxiety causes back pain by increasing muscle tension. This muscle tension can lead to pain and stiffness in the low back and upper back. Additionally, acute and chronic stress can change the way the body functions.
Anxiety can cause changes in the physical and chemical processes that occur in the body — including the way the body heals. This can cause issues like muscle tension and a slower healing process after an injury.
Stress and anxiety can also lead to other problems that can cause back pain. For example, anxiety can increase blood flow and cause blood vessels to become more inflamed, leading to problems with blood flow and swelling. Swelling in the legs, for example, can cause fluid to travel upwards and cause swelling in the back and upper back.
There are several ways to treat anxiety-related back pain. One of the most effective ways is to manage stress and anxiety but for immediate relief, you can explore using painkillers. Anxiety can be treated with a combination of psychotherapy, medication, healthy lifestyle changes, and self-help strategies.
- Exercise and Stretching:
- Engage in regular physical activity to release endorphins and improve overall health, reducing stress levels.
- Incorporate stretching routines to maintain flexibility and alleviate muscle tension.
- Perform exercises targeting core strength and posture improvement to support the back.
- Movement Breaks:
- Take short breaks during work to walk around or do a few laps around the office, promoting circulation and reducing muscle stiffness.
- Consider using a standing desk to encourage posture changes and reduce strain on the back.
- Massage Therapy:
- Utilize massage as an effective tool to alleviate both back pain and stress.
- Massage helps relax muscles, improves blood flow, and promotes a sense of relaxation.
- Yoga Practice:
- Practice yoga regularly to reduce muscle tension and back pain associated with anxiety.
- Yoga combines gentle stretching, breathing exercises, and mindfulness to enhance overall well-being.
- Warm Showers or Baths:
- Enjoy warm showers or baths to relax muscles and relieve pain caused by tension.
- Heat therapy can improve blood circulation and promote muscle relaxation.
- Alternative Therapies:
- Explore acupuncture, which may target specific points to release muscle tension and promote relaxation.
- Consider low-level laser therapy, a non-invasive treatment that stimulates healing and reduces pain.
- Mindfulness Techniques:
- Engage in mindfulness-based stress reduction techniques, such as deep breathing exercises and guided imagery.
- These practices can help manage anxiety, which in turn alleviates muscle tension and pain.
- Stress Management:
- Address the underlying stress through various approaches like therapy, meditation, or relaxation techniques.
- If the root cause of anxiety isn’t tackled, back pain may persist or worsen over time.
- Getting Enough Sleep:
- Prioritize a regular sleep schedule to ensure proper rest and recovery.
- Quality sleep promotes muscle relaxation, reduces stress, and enhances overall well-being.
- Aim for 7-9 hours of uninterrupted sleep each night.
- Eating a Healthy Diet:
- Consume a balanced diet rich in fruits, vegetables, lean proteins, and whole grains.
- Nutrient-dense foods provide the necessary vitamins and minerals for muscle function and pain management.
- Omega-3 fatty acids found in fish and nuts may have anti-inflammatory effects that benefit back health.
- Limiting Caffeine and Alcohol:
- Reduce caffeine intake, especially in the hours leading up to bedtime, to prevent sleep disturbances and muscle tension.
- Moderate alcohol consumption, as excessive drinking can disrupt sleep, exacerbate anxiety, and interfere with pain management.
- Practicing Good Posture:
- Maintain proper posture while sitting, standing, and walking to reduce strain on the back muscles.
- Use ergonomic furniture and supportive cushions to encourage healthy spinal alignment.
- Painkillers:
- Over-the-counter pain relievers like ibuprofen or acetaminophen can provide temporary relief from back pain.
- Consult a healthcare professional before using painkillers regularly, especially if you have any underlying medical conditions.
- Anxiety Medications:
- In cases where anxiety significantly contributes to back pain, anxiety medications prescribed by a doctor can help manage symptoms.
- Antidepressants and anti-anxiety medications can reduce both anxiety and the resulting muscle tension.
- Behavioral strategies are often helpful for managing anxiety. Examples include cognitive behavioral therapy (CBT) and mindfulness-based stress reduction (MBSR).
Medication can help to reduce anxiety and the associated back pain. Depending on the person, medications may include antidepressants, anti-anxiety medications, or analgesics (painkillers).
You can also use self-help strategies including breathing exercises, practicing avoidance of the stressor, and also working with other anxiety patients to get solutions that can work for you and others.
Remember, it’s essential to consult a medical professional before beginning any new exercise or treatment regimen, especially if you have pre-existing conditions or chronic pain. A comprehensive approach that combines physical, mental, and lifestyle changes will likely yield the best results in managing anxiety-related back pain.
Upper back pain and anxiety
Anxiety is a very common mental disorder that affects one in five people in their lifetime. Anxiety can cause both upper back pain and lower back pain depending on where the muscle tension is concentrated. Anxiety can cause muscle tension, either in the upper or lower back. The muscle tension from cortisol and changed breathing patterns cause pain in anxiety sufferers.
Anxiety disorders can have a significant impact on one’s life with symptoms that may include restlessness, feeling tense, feeling stressed, and being easily startled. Anxiety disorders can affect one’s health and well-being. Anxiety disorders usually first appear during childhood or adolescence, with rates steadily increasing as people get older. However, anxiety disorders can be treated. While most people with anxiety disorders are able to function at work and in relationships, they may experience certain symptoms more intensely.
These symptoms may include chest pains, headaches, upset stomach, and problems sleeping. Because anxiety disorders can affect your life in many different ways, it is important to get treatment if you think that you may be struggling with anxiety.
Can anxiety cause back pain between shoulder blades?
If you experience stress and anxiety on a regular basis, you may notice that you’re often experiencing tension in your neck and shoulders. That constant tension in those muscles can cause pain in the shoulder blades, which is known as referred pain.
Any muscle pain can cause referred pain, including the muscles in your lower back.
Emotional back pain chart
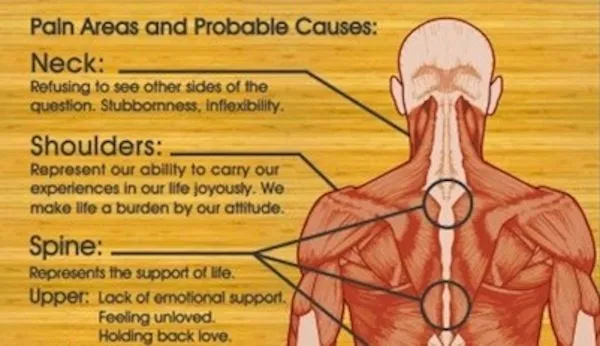
Anxiety can be caused by a combination of emotional stress and physical factors. Anxiety can affect the body in various ways, including causing back pain. While emotional stress can cause back pain, so can physical factors like poor posture or muscle spasms.
The emotional disorders that can cause back pains include anxiety (worries, stress) or depression (sadness, discouragement). The two affect the body’s chemicals, and the functions such as breathing and muscle activity causing back pain.
Regardless of the cause, it is important to identify the type of pain you are experiencing so that you can find the best treatment for it. This chart can help you determine the cause of your back pain so that you can find the best treatment for it.
Connecting Back Pain to Depression and Anxiety
If you experience anxiety or depression as a result of a traumatic event, it’s important to understand that you’re not “making up” the pain in order to receive compensation or sympathy.
If you experience intermittent back pain that goes away when you’re feeling better, it’s more likely to be a side effect of stress than a physical manifestation of your mental state.
However, if the pain is constant and unrelated to your mental state, it may be a sign that you need to seek professional help.
Can anxiety cause back pain and shortness of breath?
Anxiety can cause a number of symptoms, and one of those symptoms can be chest pain. The muscles between your ribs are likely to tighten up as a result of your anxiety (depending on where you’re experiencing anxiety), which can cause chest pain.
And since your ribs play a major role in your breathing, any pain related to those muscles may also result in shortness of breath.
Can stress cause back pains?
While it’s normal to experience some discomfort in your back as a result of stress, it’s not normal for that pain to last for extended periods of time. If you experience back pain as a result of stress, it’s likely that the pain will subside after a few days of getting some rest and taking some time to de-stress.
If the pain lasts for more than a few days (or you experience pain in your neck or upper back as well), you should consider looking into treatment options.
Lower back pain due to stress
If you have lower back pain and anxiety, it’s likely that the stress and anxiety is contributing to your existing lower back pain. The muscles that are in the lower back are responsible for holding up your spinal column, along with the weight of your upper body.
If those muscles are already strained or are experiencing chronic pain, the stress and anxiety that’s causing your upper back pain is likely adding to your lower back pain, making it worse.
Upper back pain due to stress
If you have upper back pain and anxiety, it’s likely that the stress is causing your muscles to tighten up and causing you pain. The muscles in the upper back are responsible for lifting your shoulders and holding your arms above your head.
If those muscles are already strained or are experiencing chronic pain, they will tighten as a reaction to your anxiety and stress. That tightening will cause pain in your upper back.
Conclusion
Back pain as a result of anxiety can be a serious and chronic issue. If you’re experiencing ongoing pain in your back, you may want to speak with a doctor about your symptoms.
A doctor can help you determine the root cause of your pain and help you find a treatment plan that will work for you. It’s important to note that anxiety back pain is treatable, but it’s important to seek help for it.
Chronic anxiety back pain can cause significant long-term damage to your back, which can make it difficult to cope with the mental side effects. Keep in mind that you don’t have to deal with back pain as a result of anxiety alone. There are treatments, both physical and psychological, that can help you manage your symptoms and live a normal life.
Citations:
https://www.healthline.com/health/back-pain/burning-sensation-in-upper-back